-
Review Article
- ICT-based status monitoring and anomaly detection techniques of smart greenhouse components: A review
- Md Aminur Rahman, Md Nasim Reza, Emanuel Bicamumakuba, Samsuzzaman Samsuzzaman, Hongbin Jin, Sun-Ok Chung, Soon Jung Hong
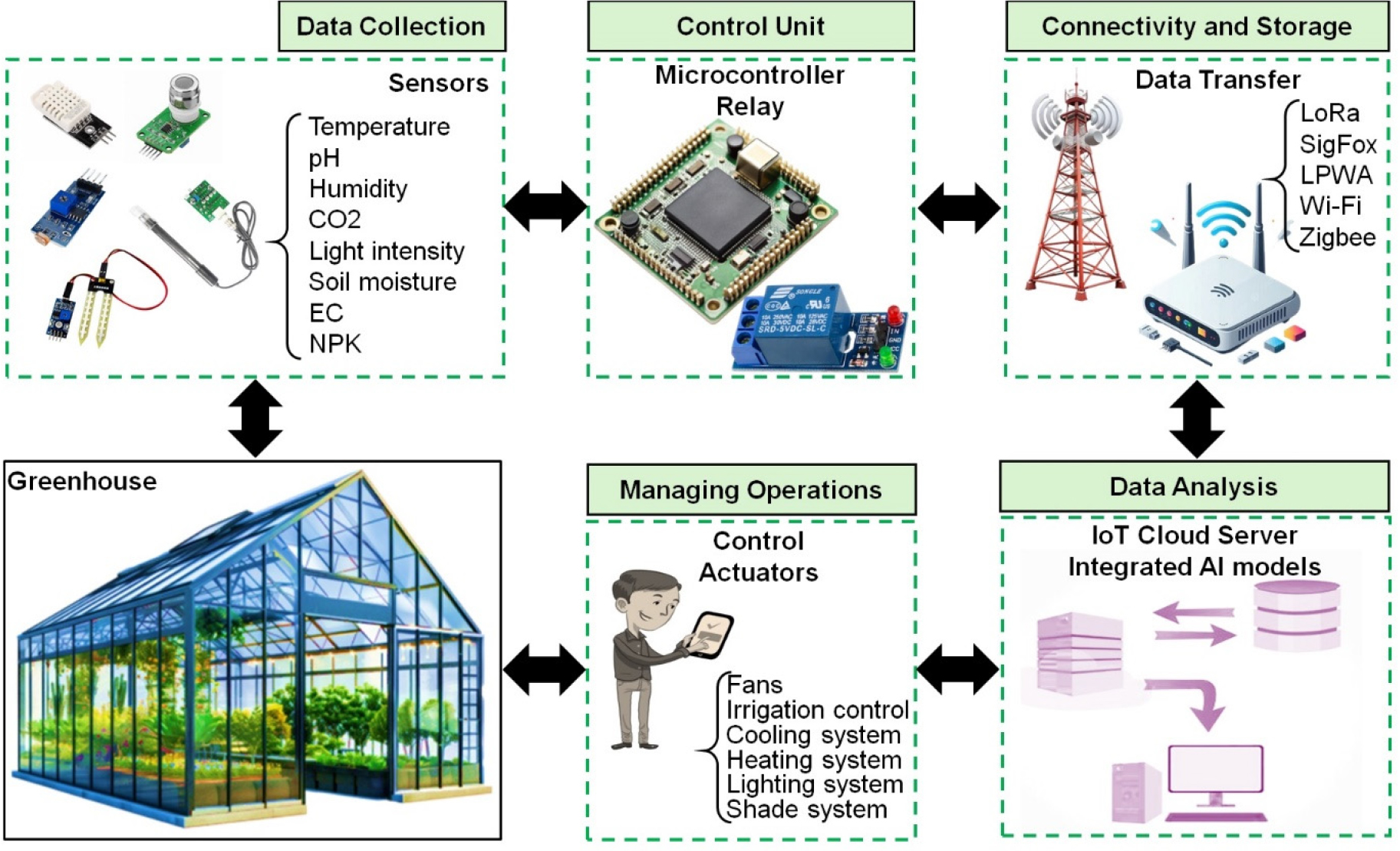
- The advancement of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) has transformed greenhouse agriculture by improving crop productivity, resource efficiency, and system sustainability. The …
- The advancement of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) has transformed greenhouse agriculture by improving crop productivity, resource efficiency, and system sustainability. The objective of this review was to provide an overview of recent advancements in ICT-enabled environmental status monitoring and anomaly detection technologies implemented in smart greenhouse components. Key technologies include Internet of Thing (IoT), Wireless Sensor Network (WSN), Machine Learning (ML)-based predictive maintenance, digital twin, and performance management. Anomaly detection approaches are analyzed across domains such as sensor fault, communication failure, and cybersecurity threat. A comparative evaluation highlights the evolution from conventional threshold-based methods to advanced ML techniques, including supervised, unsupervised, deep learning, and Edge Artificial Intelligence (AI). ML-based systems report detection accuracies up to 97%, yet challenges remain regarding data integrity, computational overhead, scalability, and adversarial robustness. Future prospects emphasize AI-based self-healing mechanism, blockchain-integrated data pipeline, 6G-enabled communication, and hybrid anomaly detection models. The study concludes that resilient ICT architectures are essential for maintaining intelligent greenhouse functionality and enhancing food security under climate variability. - COLLAPSE
-
Review Article
- A review on vision-based humanoid robot technologies: Exploring agricultural applications
- Dong hyeon Kang, Ho-seung Jang, Jayeong Paek, Seong-Woo Jeon, Sangho Lee
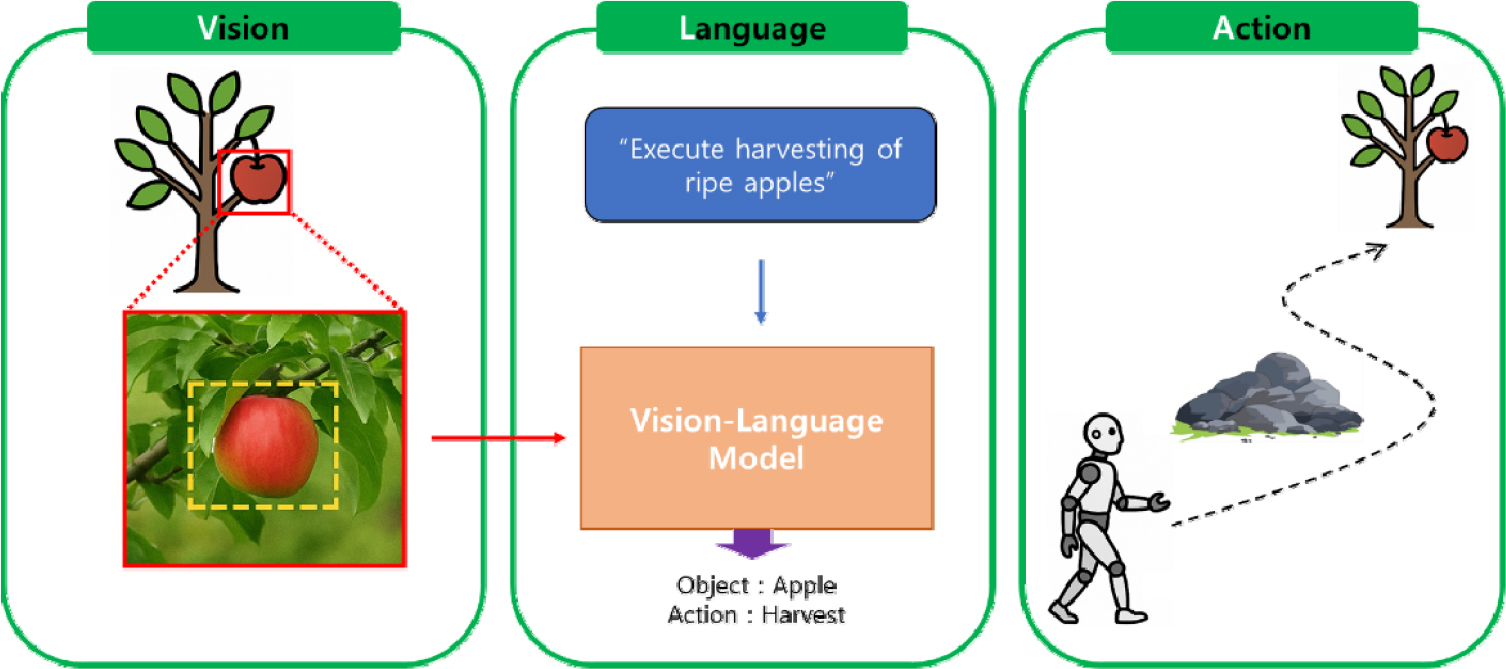
- Recent advances in artificial intelligence, sensor integration, and robotic control technologies have led to a rapid expansion of robotic applications across various …
- Recent advances in artificial intelligence, sensor integration, and robotic control technologies have led to a rapid expansion of robotic applications across various sectors. Among these, humanoid robots—characterized by human-like forms and functions—are increasingly utilized not only in industrial settings but also in healthcare, disaster response, and service industries. Within this technological trend, the agricultural sector is gaining attention as a potential frontier for humanoid robot deployment, representing the next phase of automation. Agriculture involves highly complex and unpredictable environments, including seasonal variability, where conventional fixed or wheeled automation systems often fall short. Humanoid robots, with their human-like range of motion and sensory feedback capabilities, possess the potential to flexibly adapt to such challenging conditions. This paper aims to analyze the technological potential of humanoid robots in agricultural environments. To this end, it first reviews the structural features and application cases of representative humanoid robots. It then examines technical developments centered on vision-based crop recognition and environmental perception, control algorithms including reinforcement and unsupervised learning, and multi-sensor fusion systems. Furthermore, it discusses the impact and applicability of next-generation cognitive control systems, such as the emerging Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, in agricultural robotics. This study provides a comprehensive outlook on the utilization of humanoid robots in agriculture and proposes a technological foundation for advancing precision agriculture and future human–robot collaboration systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Review Article
- Pre-harvest strategies for mitigating mycotoxins in cereal crops: Evidence and sustainable approaches
- Mohamed Kassim Giriba, Tusan Park
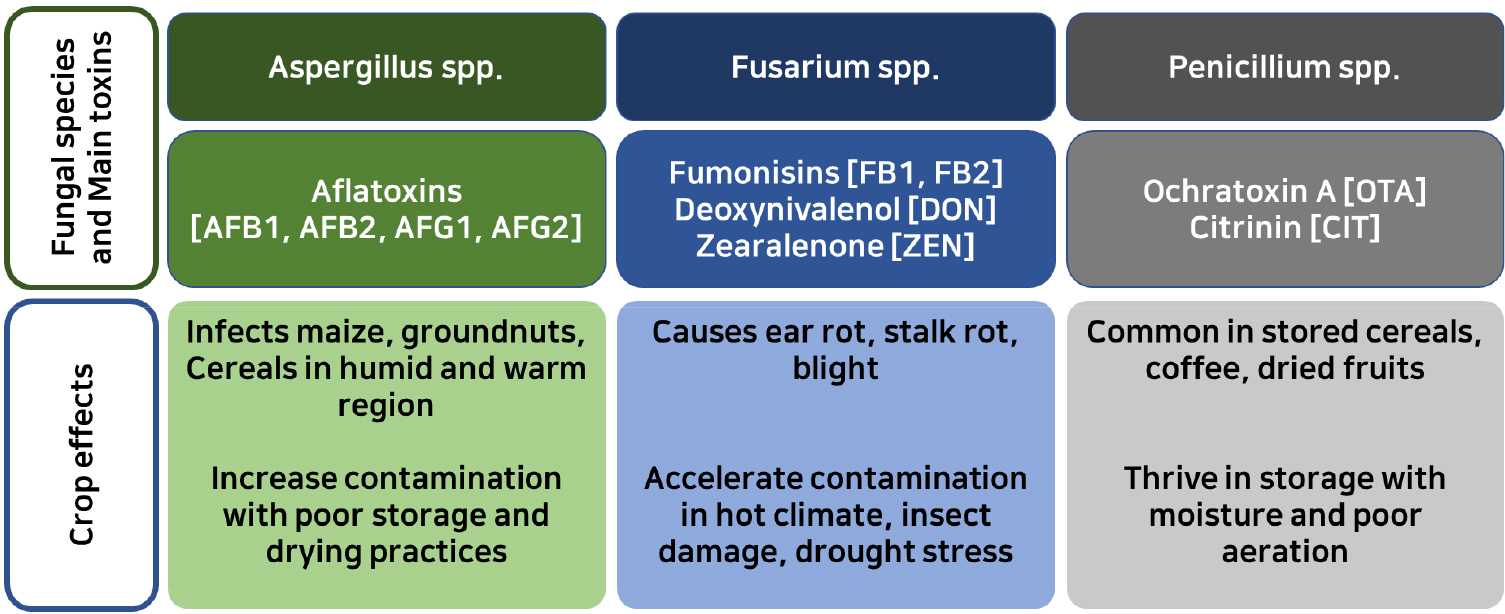
- The contamination from fungi leads to mycotoxin production and affects the well-being of humans and animals once they consume the contaminated food …
- The contamination from fungi leads to mycotoxin production and affects the well-being of humans and animals once they consume the contaminated food and feed. The toxins cause severe harmful effects, and sometimes deaths have been observed. These toxins are produced from all stages of the crop, from the growth, processing, and storage stages. This review aimed to explore how to mitigate the mycotoxin concentration from the growth stage by looking at pre-harvest interventions that can successfully find the solution. Good agricultural practices (GAP), resistant varieties, and biocontrol have successfully reduced the risk of crop contamination from the field to storage. The use of endemic atoxigenic strains as biocontrol isolate has heightened the alleviation of mycotoxins contamination with its counterpart toxigenic strains, additionally, the extrolites secreted by endemic atoxigenic strains and starch-based bioplastic formulations further reduced the extent of mycotoxins contamination. Since the contamination of cereal crops largely begins from the field, pre-harvest prevention should be a focal point to be considered to lessen the risk of mycotoxin contamination. - COLLAPSE
-
Review Article
- Advancing precision agriculture: A review of cooperative robotic systems for site-specific crop management
- Dong hyeon Kang, Jayeong Paek, Ho-seung Jang, Sangho Lee, Seong-Woo Jeon
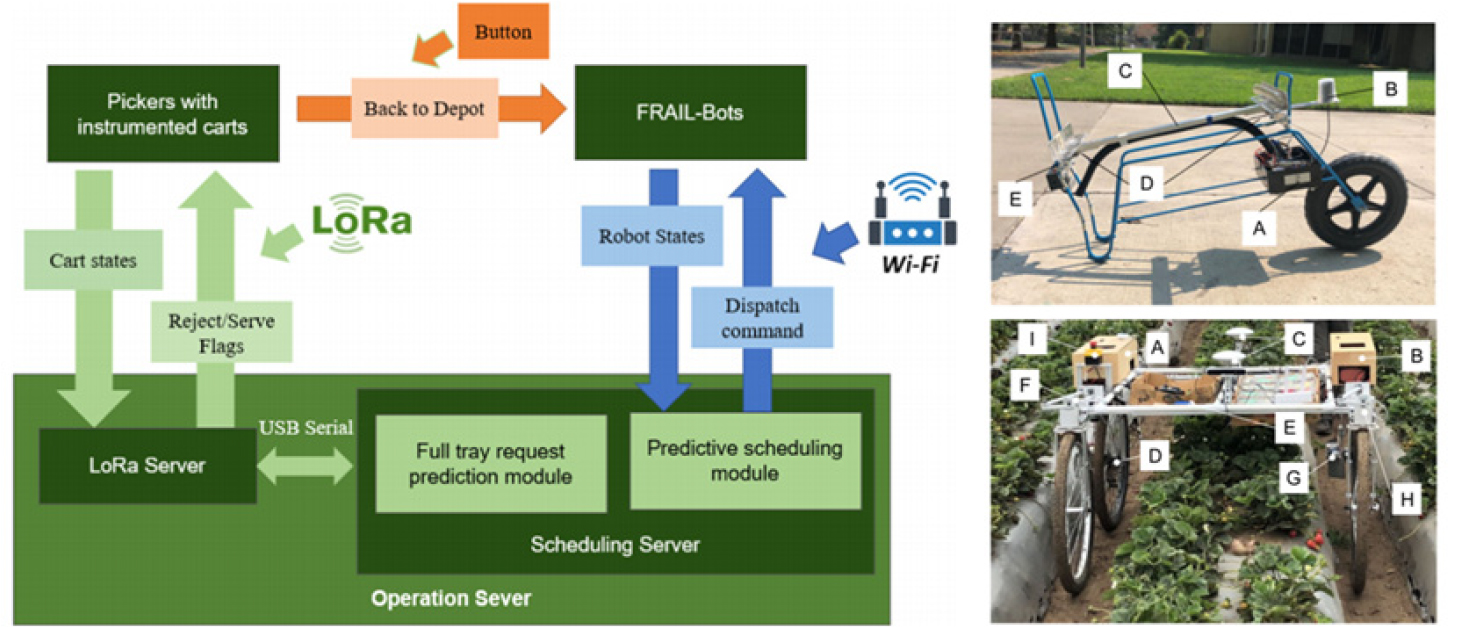
- The agricultural sector is increasingly facing challenges such as labor shortages and workforce aging, accelerating the adoption of automation and robotics in …
- The agricultural sector is increasingly facing challenges such as labor shortages and workforce aging, accelerating the adoption of automation and robotics in precision agriculture. Among emerging technologies, cooperative robots have garnered significant attention as a promising solution to enhance operational efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability in complex and unstructured farming environments. This review classifies cooperative robotics in agriculture into three categories—human–robot collaboration (HRC), multi-robot cooperation, and multi-arm robot collaboration—and systematically examines recent studies and technological developments within each domain. HRC systems focus on integrating human cognitive decision-making with robotic autonomy through shared control interfaces, activity recognition, and collaborative support systems for harvesting. Multi-robot cooperation emphasizes efficient task allocation, collision avoidance, and optimal path planning through techniques such as leader–follower control, neural network-based adaptive algorithms, and multi-task scheduling frameworks. In multi-arm robot systems, dual-manipulator configurations are utilized to improve productivity in tasks such as fruit harvesting, employing advanced trajectory planning, workspace segmentation, and role-based coordination between arms. This review provides a comprehensive understanding of the technical mechanisms and implementation strategies behind each cooperative mode, offering a foundation for the development and deployment of agricultural robotic systems. Finally, the paper identifies key research directions required for practical deployment, including structural reorganization of agricultural environments, high-precision autonomous navigation, and intelligent multi-robot task planning. The continued advancement of cooperative robotic technologies is expected to play a vital role in transitioning agriculture toward a more efficient and resilient data-driven industry. - COLLAPSE
-
Review Article
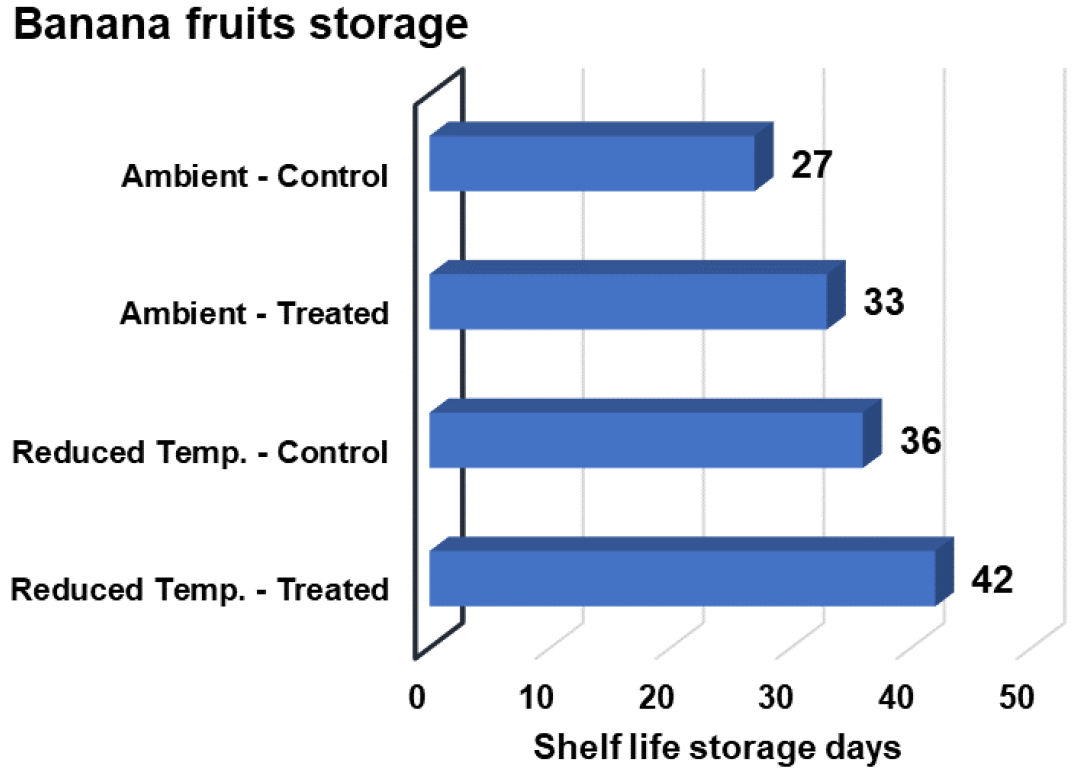
- Hexanal nanotechnology: A sustainable strategy for extending the shelf-life and preserving the quality of fruits and vegetables
- Yauba Dembo Idris, Tusan Park
- The perishable nature of fruits and vegetables makes them difficult to preserve in terms of freshness and quality, resulting in significant losses …
- The perishable nature of fruits and vegetables makes them difficult to preserve in terms of freshness and quality, resulting in significant losses along the value chain. Conventional preservation methods have constraints such as nutrient loss, short shelf-life, flavor changes, high production cost, and safety concerns. Hexanal, a naturally occurring compound, can inhibit spoilage mechanisms and extend shelf-life by suppressing ripening processes and microbial growth, offering the potential to overcome the constraints of traditional preservation techniques. This review provides insights into the principles, mechanisms, and effectiveness of hexanal nanotechnology in fruit and vegetable preservation. Recent studies demonstrated its effectiveness in extending shelf-life and preserving quality attributes are presented. Through a comprehensive review of the studies, the article highlights the potential impact of hexanal nanotechnology on the fruits and vegetables value chain. If harnessed properly, it has the capacity to improve farming productivity, decrease environmental impact, and increase the income of farmers and industry players. Biosafety studies have also indicated that hexanal and its carriers are biodegradable and do not pose a threat to the environment, making it safe for use. Moreover, challenges that need to be overcome for hexanal nanotechnology to reach its full potential in the fruit and vegetable industry, future research directions, as well as recommendations and strategies for implementation were discussed. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
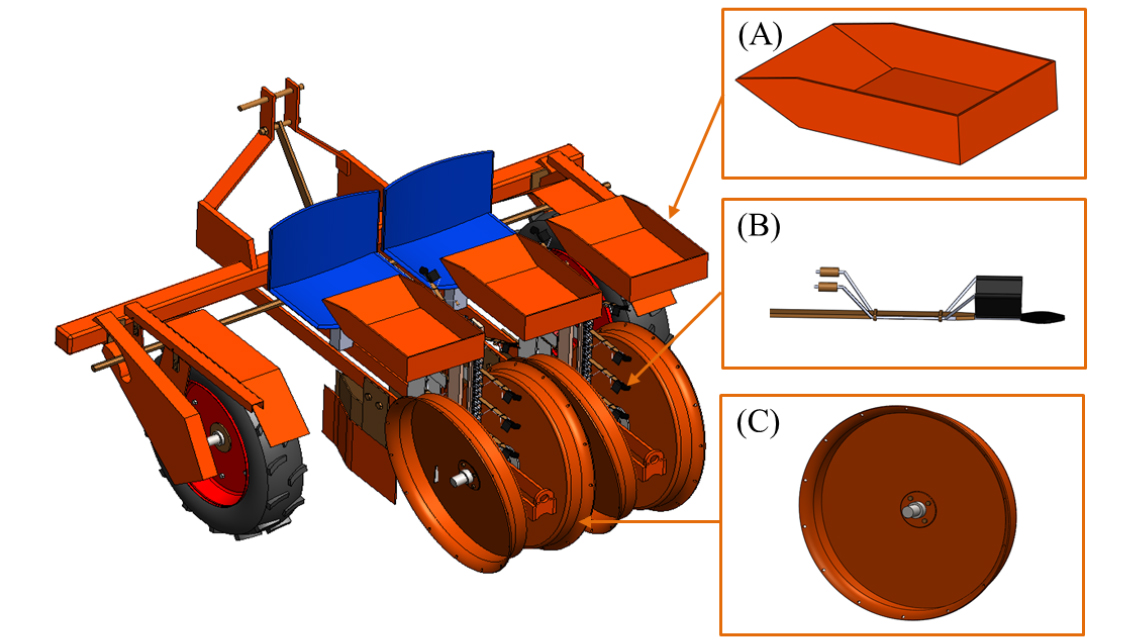
- Design and performance evaluation of a double crank five bar and finger type medicinal crop transplanter
- Md Razob Ali, Md Nasim Reza, Md Aminur Rahman, Jong Myung Choi, Kyu-Ho Lee, Sun-Ok Chung, Kanghee Jeong
- Medicinal crop cultivation in Korea holds substantial economic value and cultural significance. Nevertheless, current cultivation practices predominantly depend on labor-intensive manual transplanting …
- Medicinal crop cultivation in Korea holds substantial economic value and cultural significance. Nevertheless, current cultivation practices predominantly depend on labor-intensive manual transplanting methods. Such reliance on human labor frequently results in variable planting precision, elevated operational expenditures, and constrained scalability, posing considerable challenges to sustainable agricultural advancement. To mitigate these issues, this research introduced and evaluated two innovative transplanting mechanisms specifically customized for medicinal crops, a double-crank five-bar linkage transplanter and a finger-type bare-root transplanter. The finger-type mechanism is designed to address the handling requirements associated with delicate medicinal seedlings, whereas the five-bar linkage mechanism was optimized to facilitate higher operational speeds combined with precise trajectory control during transplanting. Both transplanters were developed using computer-aided design (CAD) modeling and evaluated under actual field conditions using Angelica gigas seedlings for finger-type transplanter and Rehmannia glutinosa seedlings or five-bar type transplanter. Key performance indicators included transplanting speed, seedling damage rate, and planting accuracy. The finger-type transplanter demonstrated a transplanting rate of 72 seedlings per minute, maintaining a low seedling damage rate of 2% and a missed planting rate of 1%. The five-bar linkage transplanter achieved a operational speed of 88 seedlings per minute, with slightly increased seedling damage and missed planting rates of 3% and 4%, respectively. These findings indicate that the five-bar linkage system is suitable for high-throughput transplanting tasks, whereas the finger-type mechanism better accommodates fragile medicinal crops that necessitate higher planting precision. This study provides valuable insights into the mechanization of medicinal crop transplanting and opportunities for developing hybrid systems that integrate the strengths of both mechanisms. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
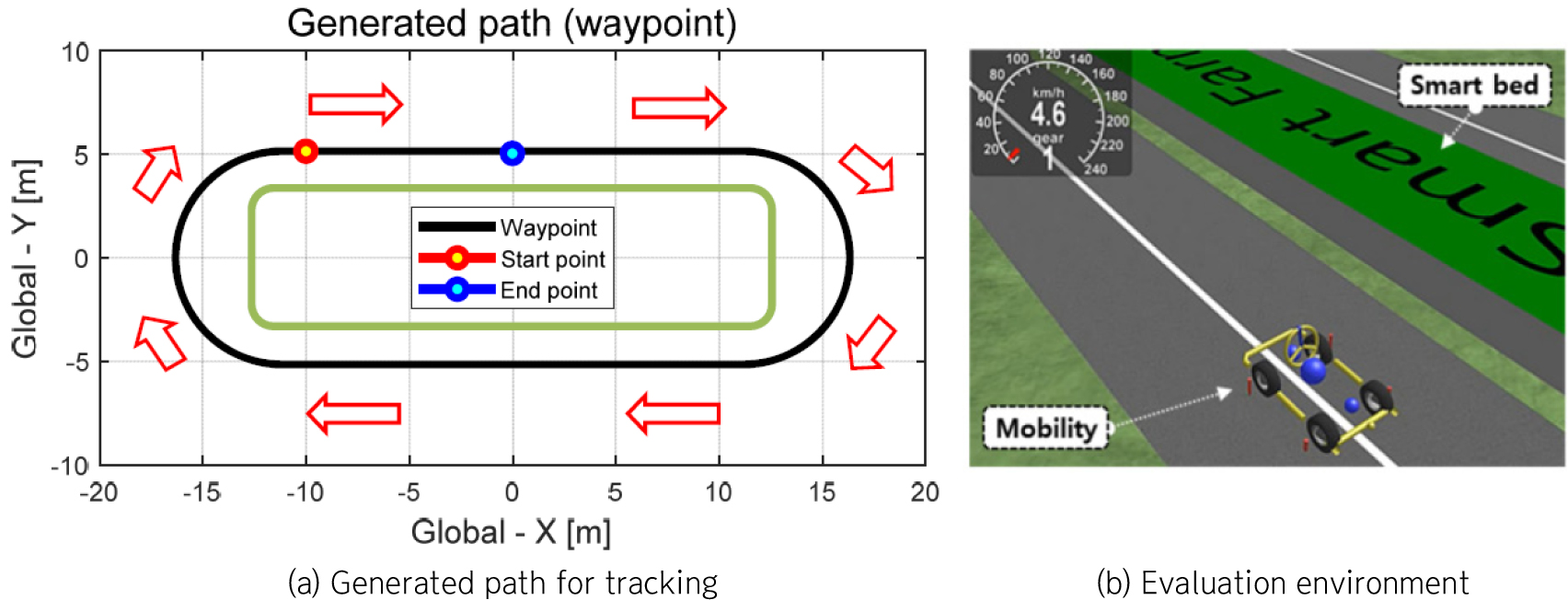
- Development of an RLS based all-wheel steering algorithm for path tracking of mobility in smart farm with gain self-tuning
- Jinseok Kang, Eungyu Lee, Donghee Ko, Wonyeop Park, Kwangseok Oh
- For improving the efficiency of crop production in smart farm, periodical monitoring of crop ripeness level and harvesting at the proper time …
- For improving the efficiency of crop production in smart farm, periodical monitoring of crop ripeness level and harvesting at the proper time are essential. For periodical monitoring of crops, this study proposes path generation and all-wheel steering control algorithms of path tracking of mobility in smart farm. Error dynamics with coefficients that represents dynamic characteristics of mobility has been designed for determination of front and rear wheel angles. The coefficients in error dynamics have been estimated based on recursive least squares with multiple forgetting factors. The estimated coefficients have been used to compute the steering control inputs in real-time based on Lyapunov direct method. To adjust the level of engagement of the rear wheel control input, parameter of reduction gain for rear wheel control input has been self-tuned using yaw angle error. The path generation algorithm for smart farm has been designed based on waypoint and it has been used for performance evaluation. The performance evaluation was conducted with the co-simulation of Matlab/Simulink and CarMaker. The results showed that the mobility can track the generated path reasonably with various evaluation cases. It was confirmed that the proposed steering control algorithm can reduce the yaw angle error with rear wheel steering. The proposed algorithm can facilitate path generation and steering control for smart farm mobility. This is expected to lead to periodic crop monitoring within smart farm facilities, automation of various tasks within smart farms, and utilization of monitoring data to control various facilities and environments, resulting in increased productivity and reduced labor costs. - COLLAPSE
-
Review Article

- Computer vision technologies for robotic harvesting and sorting automation : A reivew
- Jisu Song, Junghwa Park, Eunji Jung, Seokyung Park, Sohyeon Kang, Minjoo Kim, Gunhui Park, Jaesung Park
- Global agriculture, including that of South Korea, is facing a structural labor crisis caused by the rapid decline of the working-age population …
- Global agriculture, including that of South Korea, is facing a structural labor crisis caused by the rapid decline of the working-age population and the severe aging of farmers. In particular, the automation of harvesting and sorting, the most labor-intensive stages of agricultural production, has emerged as a critical task for ensuring long-term sustainability. This study systematically reviews recent research trends in computer vision, one of the core technologies enabling agricultural automation, and proposes directions for advancing its practical application. The review focuses on publications from 2024 to 2025 in major academic databases such as Springer, MDPI, and Elsevier, with a comprehensive examination of essential computer vision techniques for automation system development. The scope spans the entire pipeline, from data acquisition to algorithm development and field deployment, including RGB, RGB-D, and multispectral/hyperspectral imaging for data collection; YOLO-based approaches for real-time object detection; 3D perception and pose estimation; quality and ripeness assessment algorithms; and model compression and optimization for deployment on edge devices. By consolidating the current state of computer vision technologies for harvesting and sorting automation, this review provides strategic insights into future research directions, ultimately contributing to the realization of smart agriculture and the broader digital transformation of the agricultural sector. - COLLAPSE
Journal Informaiton
 Precision Agriculture Science and Technology
Precision Agriculture Science and Technology
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Precision Agriculture Science and Technology
Precision Agriculture Science and Technology











